Purge items in a large Nintex Workflow History list
IMPORTANT: This article applies to Nintex Workflow 2010,2013,2016, and 2019.
If you have more than 5,000+ records in your Nintex workflow history list, you may need to review other options to purge these items as the GUI may fail its purge operation.
History List Purge—Method 1: Use NWAdmin.exe -o PurgeHistoryListData
NWAdmin.exe is included as a part of your Nintex install. Here is an example using the PurgeHistoryListData:
SharePoint 2013 Management Shell
NWAdmin.exe –o PurgeHistoryListData -siteUrl http://yoursite.com/ -lastActivityBefore 2014-07-01 00:00 -state SELECT STATE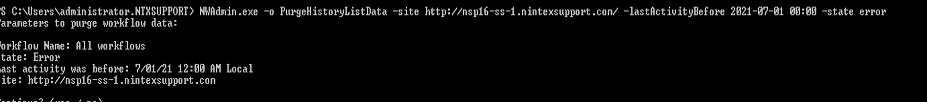
Specify to remove history list items for workflows that have a state of Running, Completed, Cancelled, Error or All state. The default is Completed if -State is left off.
Don't use -state All in production. Only purge completed workflows that you don't need to review the history of. If you purge running instance data, it will not be able to continue.
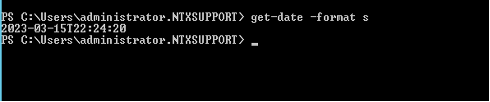
To get the correct format for the -lastActivityBefore and -lastActivityBeforeUTC switches use this command in Power-Shell:
SharePoint 2013 Management Shell
Get-Date -Format -s
Note: PurgeHistoryListData needs to be run for each Site in your Site Collection that uses Nintex Workflow. You can identify sites that have large history lists in your SharePoint farm by following the instructions in this article: How to quickly identify large lists in SharePoint
More information on NWAdmin.exe commands and switches can be found in the attachment at the end of this article. NWAdmin.exe is a command line tool that ships with Nintex Workflow 2013. It is used to perform various administration operations. The NWAdmin.exe tool is automatically deployed into the SharePoint 15 hive and can be accessed from the SharePoint 2013 Management Shell.
If the NWAdmin.exe PurgeHistoryListData approach fails to clear out items you can then try the PowerShell script below.
History List Purge—Method 2: Use PowerShell to purge items
You can find the script here: How to purge items from a large history list safely via PowerShell
This script utilizes paging and indexing to specifically target each item and delete it. Paging helps throttle the traffic to your SQL server down by only deleting X number of items at a time before it rests and starts again. Indexing enables the targeting of items without the performance overhead of enumerating and/or querying a large collection of items.
Purge large dbo.WorkflowProgress table data.
If you find you have 5,000,000 or more rows in your Nintex dbo.WorkflowProgress table then you will need to consider trimming some records. You can do this using the options below.
WARNING
Only perform a dbo.WorkflowProgress clean up AFTER you have purged data from your Nintex workflow history lists. Not doing so will prevent you from purging items from the history list using the PurgeHistoryListData command unless the -clearall switch is used.
dbo.WorkflowProgress table purge—Method 1: Use NWAdmin.exe -o PurgeWorkflowData
The recommended first step is to use the NWAdmin.exe command. Here is an example using the PurgeWorkflowData operation
SharePoint 2013 Management Shell
NWAdmin.exe -o PurgeWorkflowData -state SELECT STATE -url http://yoursite.com -lastActivityBeforeLocal 2014-07-01T00:00:00Specify to remove history list items for workflows that have a state of Running, Completed, Cancelled, Error or All state. The default is Completed if -State is left off.
Don't use -state All in production. Only purge completed workflows that you don't need to review the history of. If you purge running instance data, it will not be able to continue.
Again, you can find more information on the NWAdmin.exe command in the attachment at the end of this article.
dbo.WorkflowProgress table purge—Method 2: Use a SQL Script to purge records
If NWAdmin.exe -o PurgeWorkflowData fails to purge the records out of your dbo.WorkflowProgress table, our next recommendation is to use the following:
First you will need to gather the SiteIDs for the site collection's you would like to purge data from. To do this run the following PowerShell command:
SharePoint 2013 Management Shell
Get-SPSite -limit all | SELECT URL, ID, RootWeb
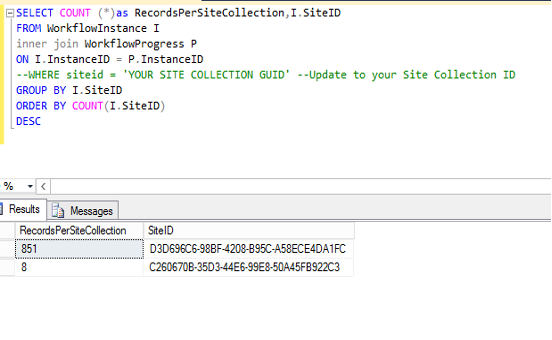
Afterword, run the following query to retrieve the number of remaining records per site collection:
SQL
SELECT COUNT (*)as RecordsPerSiteCollection,I.SiteID
FROM WorkflowInstance I
inner join WorkflowProgress P
ON I.InstanceID = P.InstanceID
--WHERE siteid = 'YOUR SITE COLLECTION GUID' --Update to your Site Collection ID
GROUP BY I.SiteID
ORDER BY COUNT(I.SiteID)
DESC
Here is an example of the output of this script:
SQL
To clear records for a specific site collection with a last activity date less than 2014-07-01. See additional filters at the bottom including doing purge per site.
SQL
DECLARE @return_value int
EXEC @return_value = [dbo].[PurgeWorkflowData]
@SiteID='YOUR SITE COLLECTION GUID', --Update to your Site Collection ID
@LastActivityDate = '2014-07-01' --Setting lastworkflowactivity time, this is actions executed older than the date specified
SELECT 'Return Value' = @return_value
GO
>You can also use one or more of the following parameters to fine-tune the query to limit the information that is removed:
SQL
@workflowname <Exact Name of workflow>
@listid <GUID>
@state <##>--Running = 2, Completed = 4, Cancelled = 8, Error = 64
@instanceid <GUID>
@webid <GUID> --Site/Sub Site
@siteid <GUID> --Site Collection
@itemid <GUID>
@lastActivityDate <Date of last activity execution>
@initiator <UserName>




